Bitcoin runs on
For an overview of cryptocurrency , start with Money is no object from We explore the early days of bitcoin and provide survey data on consumer familiarity, usage, and more. We also look at how market participants, such as investors, technology providers, and financial institutions, will be affected as the market matures. For an overview of blockchain in financial services , visit this page: Blockchain in financial services. We examine some of the ways FS firms are using blockchain, and how we expect the blockchain technology to develop in the future.
Explore how others might try to disrupt your business with blockchain technology, and how your company could use it to leap ahead instead.
Bitcoin, cryptocurrency, blockchain... So what does it all mean?
Blockchain announcements continue to occur, although they are less frequent and happen with less fanfare than they did a few years ago. Still, blockchain technology has the potential to result in a radically different competitive future for the financial services industry. Contact us to learn more about what PwC Financial Services can do for you. Any blockchain solution, no matter how prescient, is only as good as its execution. This is where PwC excels—by offering proven expertise in managing complex implementation programs from start to finish. Learn more. All rights reserved. PwC refers to the US member firm or one of its subsidiaries or affiliates, and may sometimes refer to the PwC network.
Each member firm is a separate legal entity. Please see www. Bitcoin, cryptocurrency, blockchain However, Bitcoin is not alone. At this moment, there are over AltCoin implementations, which use similar principles and various cryptocurrency algorithms. Fulfilling the first two requirements from our list, removing a central authority for information exchange over the Internet, is already possible. What you need is a peer-to-peer P2P network. Information sharing in P2P networks is similar to information sharing among friends and family.
If you share information with at least one member of the network, eventually this information will reach every other member of the network. The only difference is that in digital networks this information will not be altered in any way. You have probably heard of BitTorrent, one of the most popular P2P file sharing content delivery systems.
Another popular application for P2P sharing is Skype, as well as other chat systems. To understand digital identities, we need to understand how cryptographic hashing works. Hashing is the process of mapping digital data of any arbitrary size to data of a fixed size.
Quantum computers and the Bitcoin blockchain
In simpler words, hashing is a process of taking some information that is readable and making something that makes no sense at all. You can compare hashing to getting answers from politicians.
Information you provide to them is clear and understandable, while the output they provide looks like random stream of words. If you take a look at the simple statistics, we will have a limited but huge number of possible HASH values, simply because our HASH length is limited. If you think Hamlet is just a name or a word, please stop reading now, or read about the Infinite Monkey Theorem. When signing a paper, all you need to do is append your signature to the text of a document.
A digital signature is similar: you just need to append your personal data to the document you are signing. If you understand that the hashing algorithm adheres to the rule where even the smallest change in input data must produce significant difference in output , then it is obvious that the HASH value created for the original document will be different from the HASH value created for the document with the appended signature.
A combination of the original document and the HASH value produced for the document with your personal data appended is a digitally signed document. And this is how we get to your virtual identity , which is defined as the data you appended to the document before you created that HASH value. Next, you need to make sure that your signature cannot be copied, and no one can execute any transaction on your behalf.
How does Bitcoin work? - Bitcoin
The best way to make sure that your signature is secured, is to keep it yourself, and provide a different method for someone else to validate the signed document. Again, we can fall back on technology and algorithms that are readily available. What we need to use is public-key cryptography also known as asymmetric cryptography.
To make this work, you need to create a private key and a public key. These two keys will be in some kind of mathematical correlation and will depend on each other.
The algorithm that you will use to make these keys will assure that each private key will have a different public key. As their names suggest, a private key is information that you will keep just for yourself, while a public key is information that you will share. If you use your private key your identity and original document as input values for the signing algorithm to create a HASH value, assuming you kept your key secret, you can be sure that no one else can produce the same HASH value for that document. If anyone needs to validate your signature, he or she will use the original document, the HASH value you produced, and your public key as inputs for the signature verifying algorithm to verify that these values match.
Assuming that you have implemented P2P communication, mechanisms for creating digital identities private and public keys , and provided ways for users to sign documents using their private keys, you are ready to start sending information to your peers. Since we do not have a central authority that will validate how much money you have, the system will have to ask you about it every time, and then check if you lied or not. So, your transaction record might contain the following information:. The only thing left to do is digitally sign the transaction record with your private key and transmit the transaction record to your peers in the network.
Your job is done. However, your medication will not be paid for until the whole network agrees that you really did have coins, and therefore could execute this transaction. Only after your transaction is validated will your pharmacist get the funds and send you the medication. Miners are known to be very hard working people who are, in my opinion, heavily underpaid. In the digital world of cryptocurrency, miners play a very similar role, except in this case, they do the computationally-intensive work instead of digging piles of dirt.
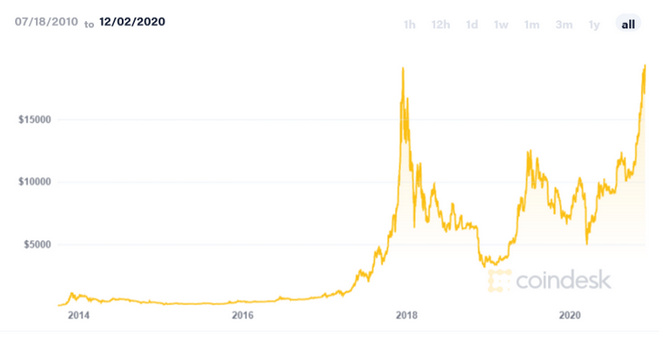
Unlike real miners, some cryptocurrency miners earned a small fortune over the past five years, but many others lost a fortune on this risky endeavour.
- tax on bitcoin purchase!
- Welcome back!
- coinbase bitcoin instant buy.
- what us mining bitcoin.
- blockchain price of bitcoin!
- Bitcoin Bull Run: OGs on Why This One’s Different!
- What Is Bitcoin Mining | Fortinet;
Miners are the core component of the system and their main purpose is to confirm the validity of each and every transaction requested by users. In order to confirm the validity of your transaction or a combination of several transactions requested by a few other users , miners will do two things.
They will look into the history of your transactions to verify that you actually had coins to begin with. Once your account balance is confirmed, they will generate a specific HASH value. This hash value must have a specific format; it must start with certain number of zeros.
Going down the rabbit hole
Considering that even the smallest change in input data must produce a significant difference in output HASH value , miners have a very difficult task. They need to find a specific value for a proof-of-work variable that will produce a HASH beginning with zeros.
Once a miner finds the proper value for proof-of-work, he or she is entitled to a transaction fee the single coin you were willing to pay , which can be added as part of the validated transaction. Every validated transaction is transmitted to peers in the network and stored in a specific database format known as the Blockchain. But what happens if the number of miners goes up, and their hardware becomes much more efficient?
- bitcoin company colorado!
- Navigation menu!
- Bitcoin - Wikipedia?
- Why does Bitcoin need more energy than whole countries?!
- how much bitcoin cash will i get!
- More from Jamie.
- Bitcoin network - Wikipedia;
As the hash rate goes up, so does the mining difficulty, thus ensuring equilibrium. When more hashing power is introduced into the network, the difficulty goes up and vice versa; if many miners decide to pull the plug because their operation is no longer profitable, difficulty is readjusted to match the new hash rate. The blockchain contains the history of all transactions performed in the system. Every validated transaction, or batch of transactions, becomes another ring in the chain.